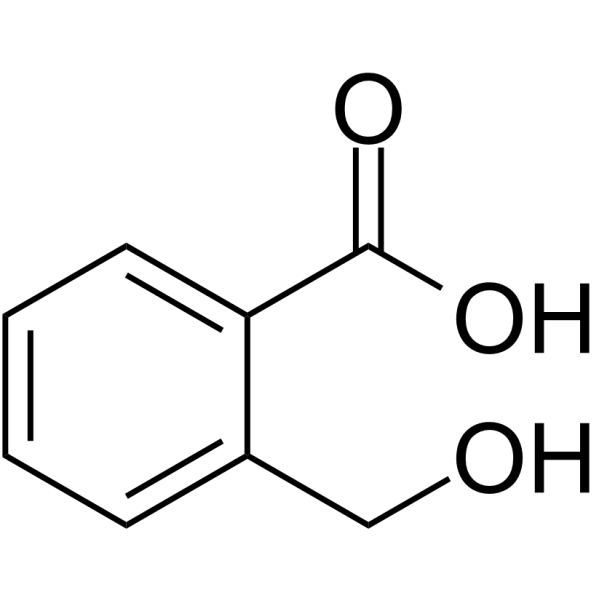
2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid
CAS No. 612-20-4
2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M28090 CAS No. 612-20-4
2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid is a principal metabolite of the phthalidyl moiety in man.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid is a principal metabolite of the phthalidyl moiety in man.
-
Description2-hydroxymethyl benzoic acid is a principal metabolite of the phthalidyl moiety in man.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
Recptorp38α|p38β
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number612-20-4
-
Formula Weight152.149
-
Molecular FormulaC8H8O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (657.25 mM)
-
SMILESOCc1ccccc1C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Balagué C, et al. Profiling of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, p38 and JAK inhibitors in the rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model: a translational study. Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;166(4):1320-32.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Acetamide
Acetamide is found in red beetrootis used primarily as a solvent and a plasticizer.
-
p-Cresyl sulfate pot...
p-Methylphenyl potassium sulfate is a prototype protein-bound uremic toxin derived from the metabolites of tyrosine and phenylalanine through liver.
-
Campesterol
Campesterol is a plant sterol with cholesterol lowering and anticarcinogenic effects, it and other plant sterols often decrease LDL cholesterol levels overall. Campesterol has anti-inflammatory effect, it inhibits several pro-inflammatory and matrix degradation mediators typically involved in osteoarthritis- induced cartilage degradation, also sometimes used to treat some specific prostate conditions.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


